🏢 Ingenium – The Specialized Insurance Core System
Ingenium is the core system for the insurance industry, designed to comprehensively manage complex business processes—from request intake and policy processing to claims payment. For years, Ingenium has been a solid foundation, ensuring stability, security, and compliance with the stringent standards of the finance and insurance sectors.
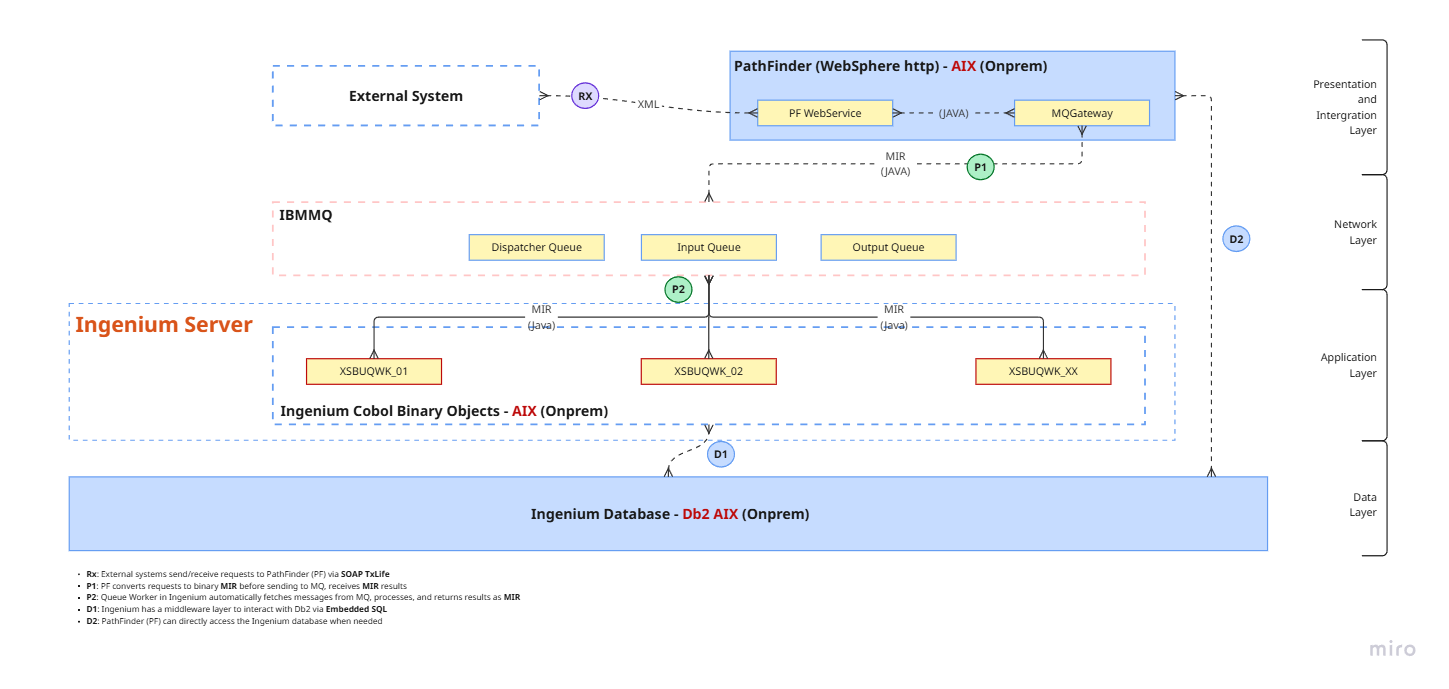
🗺️ Architecture Overview
Ingenium is deployed on-premise on the AIX platform with a Db2 database. Its architecture is clearly separated into functional layers, optimizing system maintenance and scalability:
- Presentation & Integration Layer: User interface, external system integration.
- Network Layer: Coordination and communication between components.
- Application Layer: Insurance business logic processing.
- Data Layer: Storage and management of business data.
Main Components
🌐 PathFinder
- Presentation & Integration Layer: UI Server and integration gateway.
- Developed in Java, deployed on WebSphere HTTP Server (AIX On-premise).
- Supports flexible customization to meet the business requirements of each enterprise.
📦 MQ Server
- Network Layer: Central coordinator and communication hub between components.
- Manages queues (Dispatcher Queue, Input Queue, Output Queue), ensuring sequential and accurate processing.
- Acts as a bridge between PathFinder and Ingenium, using MIR messages (binary COBOL Copybook).
⚙️ Ingenium
- Application Layer: The "business core" – the center for insurance business logic processing.
- Multiple COBOL modules running on AIX, ensuring high performance and stability.
- Initializes multiple independent "queue workers" (e.g., XSBUQWK) to proactively fetch requests from MQ, process them, and return results via the MIR format.
🗄️ Ingenium Database
- Data Layer: Db2 AIX (On-premise) stores all business data.
- COBOL modules interact via the dbsrce layer, ensuring efficiency and data safety.
- External systems (including PathFinder) can access the database directly when needed.
🔗 External Systems
External systems integrate with Ingenium via PathFinder (SOAP TxLife) to exchange insurance business information, ensuring security and industry standard compliance.
✅ A Solid Legacy Foundation
Ingenium delivers time-tested core values, serving as the bedrock for the operations of many insurance enterprises.
- Stable and Reliable: Built on proven technologies in the financial industry, ensuring the system operates with enduring stability.
- Handles Complex Business Logic: Capable of meeting diverse and in-depth insurance business requirements.
- Maximum Security: The on-premise model and centralized data allow for the highest level of security control.
- High-Volume Performance: The parallel queue/worker architecture efficiently handles large volumes of transactions.
- Compliance and Auditing: Facilitates easy transaction tracing, meeting the strict audit requirements of the industry.
⚠️ The Challenges of a Legacy System
However, as technology evolves, Ingenium reveals inherent limitations that have become barriers to digital transformation.
- Outdated Technology: The COBOL and AIX platform, along with components of the IBM ecosystem (MQ, WebSphere), are obsolete, face a shortage of skilled personnel, and are no longer fully supported.
- Difficult to Scale & High Costs: The rigid on-premise model is expensive to operate and difficult to scale quickly in response to market demands.
- Limited Integration: A lack of modern protocols like API/REST makes it difficult to connect with digital services and partner ecosystems.
- Manual Processes: Deployment, version management, and rollbacks are performed manually, lacking automation (DevOps), which slows down the pace of innovation.
- Barrier to Digital Transformation: Struggles to meet demands for multi-channel integration, big data analytics, and the deployment of new digital services.
🚀 The Inevitable Path to Transformation
These challenges demand a strategic and comprehensive transformation roadmap. This is no longer an option but a mandatory requirement for businesses to survive and thrive in the digital age.
- Technology Modernization: Migrating from COBOL to modern languages and upgrading the platform to enhance integration capabilities.
- Cloud/Hybrid Transition: Adopting a flexible model to optimize costs, increase scalability, and leverage the power of cloud computing.
- Comprehensive Automation (DevOps): Building CI/CD pipelines to accelerate development, deployment, and reduce risks.
This is precisely the mission that the Binean Nova project was created to address.
📄 Legal Disclaimer
This document is provided for reference and consulting purposes regarding system integration and transformation solutions.
All trademarks, product names, and company names mentioned herein are the property of their respective owners.
This project is not affiliated with, sponsored by, or endorsed by DXC Technology, Sun Life, or any other third party mentioned.
No source code, license, or proprietary information of Ingenium or any third-party system is provided or distributed as part of this documentation or related services.
By using or referencing this document, you acknowledge and agree to comply with all applicable intellectual property laws and the terms stated above.
Glossary:
- On-premise: System deployed on the enterprise's physical server infrastructure, not cloud-based.
- COBOL: A long-standing programming language, popular in finance – banking, insurance.
- MQ (IBM MQ): Middleware message queue system, facilitates communication between components.
- SOAP TxLife: Insurance data exchange standard over SOAP protocol.
- AIX: IBM's UNIX operating system for enterprise servers.
- MIR: A binary message format based on COBOL Copybook, used for communication between Ingenium components.